Demo | GitHub | Hugging Face | Technical Report |🔥Official Website

引言
PaddleOCR-VL-1.5 是 PaddleOCR-VL 的一次重要升级,在 OmniDocBench v1.5 上达到了 94.5% 的全新 SOTA 准确率。为了系统性评估模型在真实世界物理畸变条件下的鲁棒性(包括扫描伪影、倾斜、弯折、屏幕拍照以及光线变化),我们提出了 Real5-OmniDocBench 基准。实验结果表明,该增强模型在这一全新构建的基准上同样取得了 SOTA 表现。此外,我们在保持 0.9B 超紧凑 VLM 与高推理效率的前提下,进一步扩展了模型能力,引入了 印章识别(Seal Recognition) 与 文本检测识别一体化(Text Spotting) 等任务。
PaddleOCR-VL-1.5 的核心能力
- 在仅 0.9B 参数规模下,PaddleOCR-VL-1.5 在 OmniDocBench v1.5 上取得 94.5% 准确率,超越此前的 SOTA 模型 PaddleOCR-VL,并在 表格、公式与文本识别 等任务上取得显著提升。
- 提出了一种 支持不规则形状定位的文档解析新范式,能够在文档倾斜、弯折等复杂条件下进行精确的多边形检测。在扫描、倾斜、弯折、屏幕拍照与光线变化五类真实场景评测中,整体性能显著优于主流开源与商用模型。
- 新增 文本检测识别一体化(文本行级定位 + 识别) 与 印章识别 能力,并在对应任务指标上均刷新 SOTA。
- 在 专业场景与多语言识别能力 上进一步增强:针对 古籍文本、多语言表格、下划线与复选框 的识别效果显著提升,并新增对 藏文与孟加拉文 的语言支持。
- 支持 跨页表格自动合并 与 跨页段落标题识别,有效缓解 长文档解析 中的内容割裂问题。
模型架构
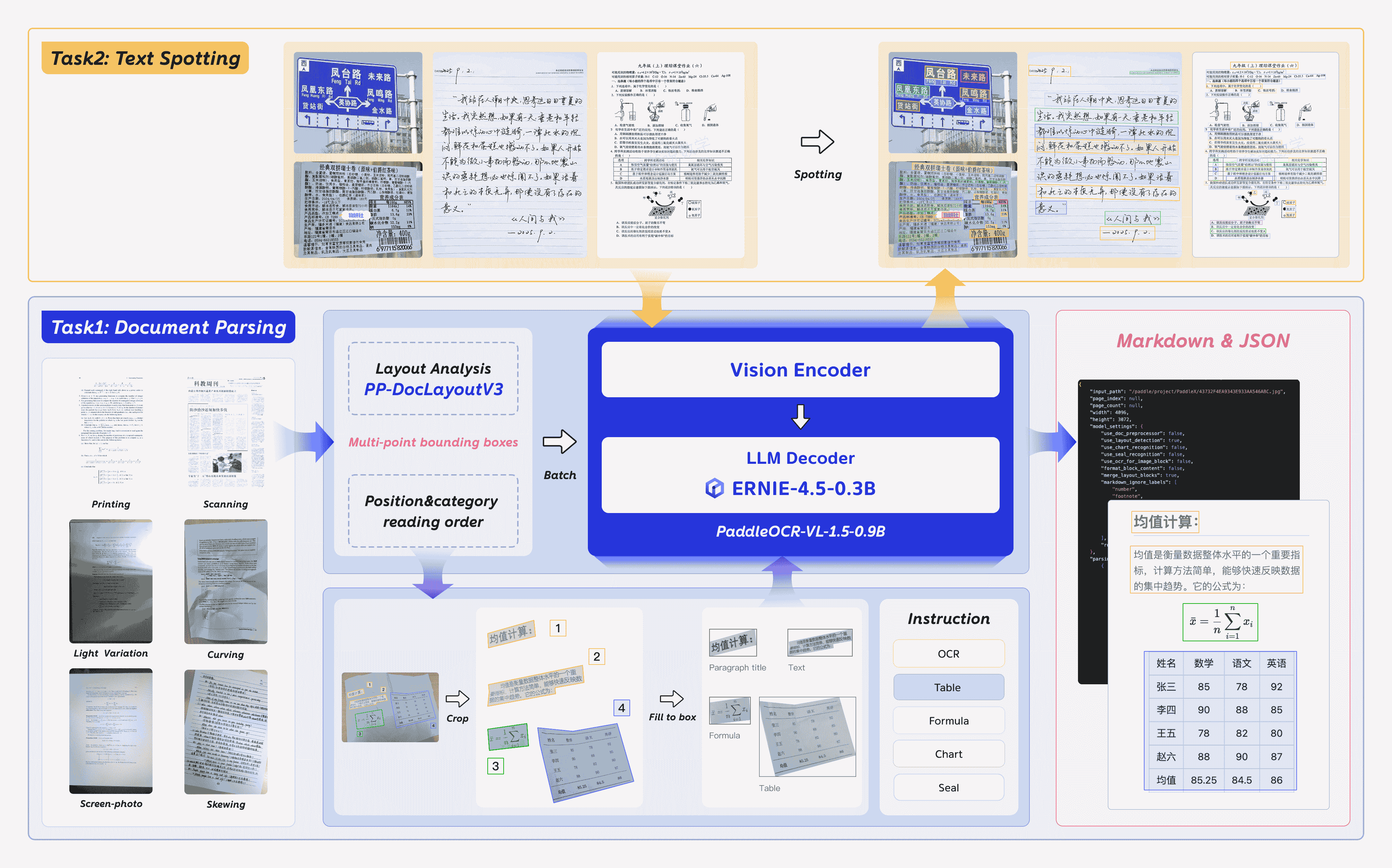
使用方法
安装依赖
安装 PaddlePaddle 与 PaddleOCR:
# The following command installs the PaddlePaddle version for CUDA 12.6. For other CUDA versions and the CPU version, please refer to https://www.paddlepaddle.org.cn/en/install/quick?docurl=/documentation/docs/en/develop/install/pip/linux-pip_en.html
python -m pip install paddlepaddle-gpu==3.2.1 -i https://www.paddlepaddle.org.cn/packages/stable/cu126/
python -m pip install -U "paddleocr[doc-parser]"
请确保安装 PaddlePaddle 3.2.1 或更高版本,并搭配特殊版本的 safetensors。 macOS 用户请使用 Docker 搭建环境。
基础用法
CLI:
paddleocr doc_parser -i https://paddle-model-ecology.bj.bcebos.com/paddlex/imgs/demo_image/paddleocr_vl_demo.png
Python API:
from paddleocr import PaddleOCRVL
pipeline = PaddleOCRVL()
output = pipeline.predict("https://paddle-model-ecology.bj.bcebos.com/paddlex/imgs/demo_image/paddleocr_vl_demo.png")
for res in output:
res.print()
res.save_to_json(save_path="output")
res.save_to_markdown(save_path="output")
通过优化推理服务加速 VLM 推理
-
启动 VLM 推理服务:
可以用以下两种方式启动 vLLM 推理服务:
-
方法 1:PaddleOCR 方式
docker run \ --rm \ --gpus all \ --network host \ ccr-2vdh3abv-pub.cnc.bj.baidubce.com/paddlepaddle/paddleocr-genai-vllm-server:latest-nvidia-gpu \ paddleocr genai_server --model_name PaddleOCR-VL-1.5-0.9B --host 0.0.0.0 --port 8080 --backend vllm -
方法 2:vLLM 方式
-
-
调用 PaddleOCR CLI 或 Python API:
paddleocr doc_parser \ -i https://paddle-model-ecology.bj.bcebos.com/paddlex/imgs/demo_image/paddleocr_vl_demo.png \ --vl_rec_backend vllm-server \ --vl_rec_server_url http://127.0.0.1:8080/v1from paddleocr import PaddleOCRVL pipeline = PaddleOCRVL(vl_rec_backend="vllm-server", vl_rec_server_url="http://127.0.0.1:8080/v1") output = pipeline.predict("https://paddle-model-ecology.bj.bcebos.com/paddlex/imgs/demo_image/paddleocr_vl_demo.png") for res in output: res.print() res.save_to_json(save_path="output") res.save_to_markdown(save_path="output")
更多用法与参数说明请参阅 文档。
使用 transformers 库推理 PaddleOCR-VL-1.5-0.9B
当前 PaddleOCR-VL-1.5-0.9B 支持通过 transformers 库进行无缝推理,覆盖 文本检测识别一体化,以及公式、表格、图表与印章等复杂元素识别。下面提供一个基于 transformers 的简单示例脚本。
注:当前仍推荐使用官方推理方式,其速度更快,并支持页面级文档解析。以下示例仅支持元素级识别与文本检测识别一体化。
# ensure the transformers v5 is installed
python -m pip install "transformers>=5.0.0"
from PIL import Image
import torch
from transformers import AutoProcessor, AutoModelForImageTextToText
# ---- Settings ----
model_path = "PaddlePaddle/PaddleOCR-VL-1.5"
image_path = "test.png"
task = "ocr" # Options: 'ocr' | 'table' | 'chart' | 'formula' | 'spotting' | 'seal'
# ------------------
# ---- Image Preprocessing For Spotting ----
image = Image.open(image_path).convert("RGB")
orig_w, orig_h = image.size
spotting_upscale_threshold = 1500
if task == "spotting" and orig_w < spotting_upscale_threshold and orig_h < spotting_upscale_threshold:
process_w, process_h = orig_w * 2, orig_h * 2
try:
resample_filter = Image.Resampling.LANCZOS
except AttributeError:
resample_filter = Image.LANCZOS
image = image.resize((process_w, process_h), resample_filter)
# Set max_pixels: use 1605632 for spotting, otherwise use default ~1M pixels
max_pixels = 2048 * 28 * 28 if task == "spotting" else 1280 * 28 * 28
# ---------------------------
# -------- Inference --------
DEVICE = "cuda" if torch.cuda.is_available() else "cpu"
PROMPTS = {
"ocr": "OCR:",
"table": "Table Recognition:",
"formula": "Formula Recognition:",
"chart": "Chart Recognition:",
"spotting": "Spotting:",
"seal": "Seal Recognition:",
}
model = AutoModelForImageTextToText.from_pretrained(model_path, torch_dtype=torch.bfloat16).to(DEVICE).eval()
processor = AutoProcessor.from_pretrained(model_path)
messages = [
{
"role": "user",
"content": [
{"type": "image", "image": image},
{"type": "text", "text": PROMPTS[task]},
]
}
]
inputs = processor.apply_chat_template(
messages,
add_generation_prompt=True,
tokenize=True,
return_dict=True,
return_tensors="pt",
images_kwargs={"size": {"shortest_edge": processor.image_processor.min_pixels, "longest_edge": max_pixels}},
).to(model.device)
outputs = model.generate(**inputs, max_new_tokens=512)
result = processor.decode(outputs[0][inputs["input_ids"].shape[-1]:-1])
print(result)
# ---------------------------
可选项:使用 flash-attn 提升性能并降低显存占用
# ensure the flash-attn2 is installed
pip install flash-attn --no-build-isolation
model = AutoModelForImageTextToText.from_pretrained(model_path, torch_dtype=torch.bfloat16, attn_implementation="flash_attention_2").to(DEVICE).eval()
性能表现
文档解析
1. OmniDocBench v1.5
PaddleOCR-VL-1.5 在 OmniDocBench v1.5 的整体指标、文本、公式、表格与阅读顺序等维度上均取得 SOTA 表现。

注:
性能指标来自 OmniDocBench 官方排行榜,其中 Gemini-3 Pro、Qwen3-VL-235B-A22B-Instruct 以及 PaddleOCR-VL-1.5 为独立评测。
2. Real5-OmniDocBench
在扫描、形变、屏幕拍摄、光照与倾斜五类复杂场景上,PaddleOCR-VL-1.5 持续刷新 SOTA 纪录。

注:
Real5-OmniDocBench 是一个面向真实世界场景的全新基准,我们基于 OmniDocBench v1.5 数据集构建。该数据集包含五类场景:扫描、弯折、屏幕拍照、光线变化与倾斜。更多细节请参阅 Real5-OmniDocBench。
推理性能
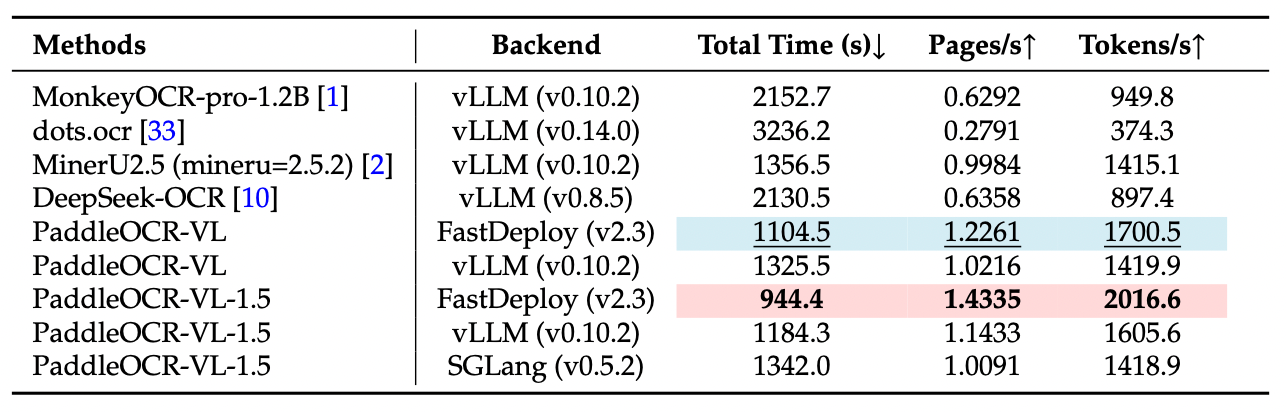
注:
OmniDocBench v1.5 上的端到端推理性能对比。PDF 文档在单张 NVIDIA A100 GPU 上以 batch size=512 进行推理。统计时间包含 PDF 渲染与 Markdown 生成。所有方法均使用各自默认 PDF 解析模块与 DPI 设置,以反映开箱即用的真实性能。
可视化示例
以下是一些 真实场景文档解析 示例。
光线变化

倾斜

屏幕拍摄

扫描

弯折

文本检测识别一体化

印章识别

致谢
感谢 PaddleFormers、Keye、MinerU、OmniDocBench 提供宝贵的代码、模型权重与基准。也感谢社区的每一位贡献者!
引用
如果你觉得 PaddleOCR-VL-1.5 有帮助,欢迎给我们点 Star 并引用。
@misc{cui2026paddleocrvl15multitask09bvlm,
title={PaddleOCR-VL-1.5: Towards a Multi-Task 0.9B VLM for Robust In-the-Wild Document Parsing},
author={Cheng Cui and Ting Sun and Suyin Liang and Tingquan Gao and Zelun Zhang and Jiaxuan Liu and Xueqing Wang and Changda Zhou and Hongen Liu and Manhui Lin and Yue Zhang and Yubo Zhang and Yi Liu and Dianhai Yu and Yanjun Ma},
year={2026},
eprint={2601.21957},
archivePrefix={arXiv},
primaryClass={cs.CV},
url={https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.21957},
}